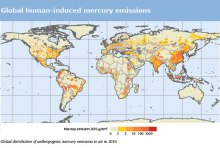
Special Issue on International Chemicals Regulation Following the Minamata Convention
Legal frameworks are one main way through which chemicals are defined: terms of harm, responsibility, and circulation, some of the defining features of pollution, are debated, agreed upon, and codified in legal forums. The Minamanta Convention on Mercury is the first environmental agreement in a decade to set these terms across nations.